- Overview
Introduction
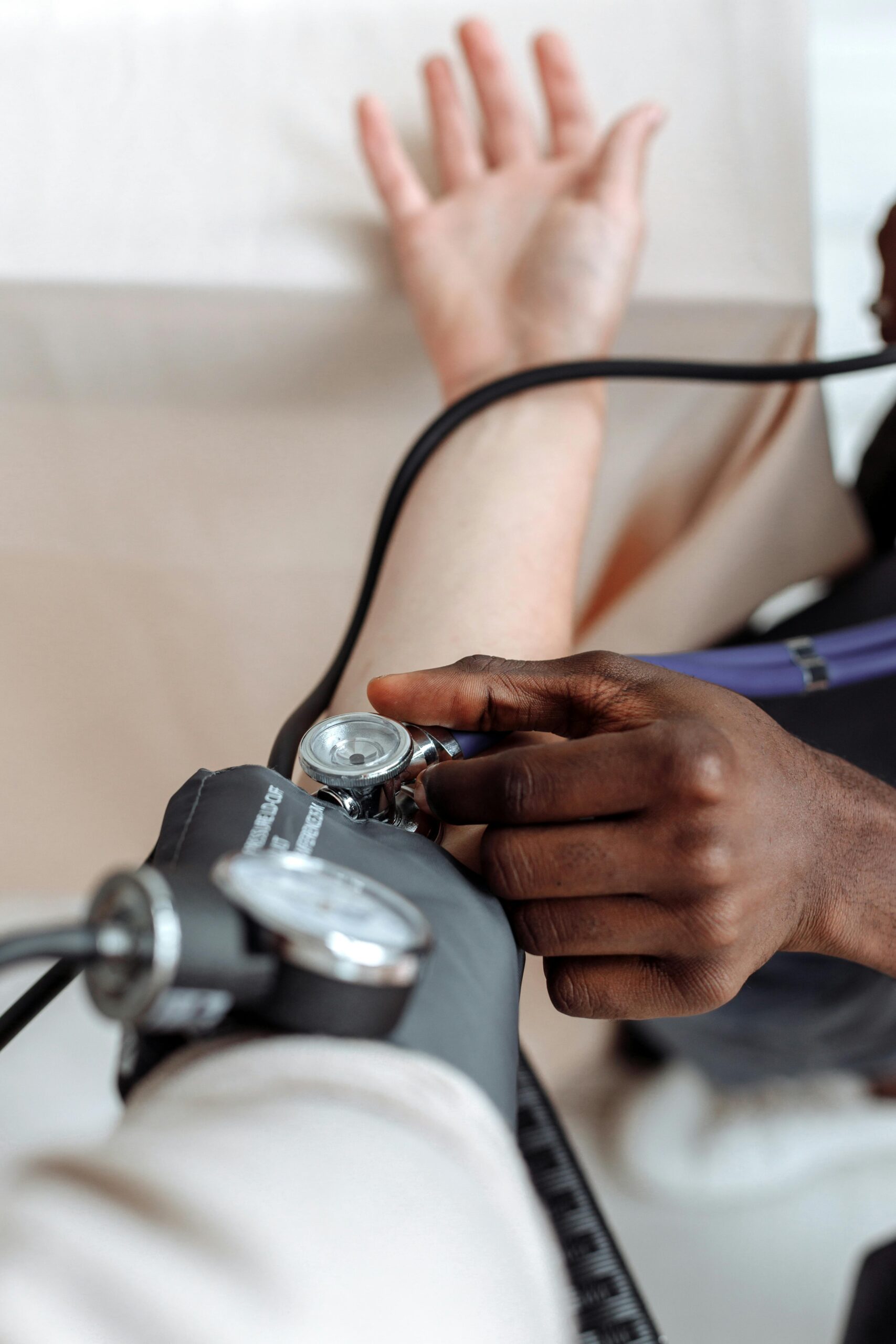
Vital signs are essential indicators of a person’s health status and physiological functions. They provide critical information that helps healthcare professionals assess a patient’s condition, detect potential health issues, and monitor the effectiveness of treatments. The four primary vital signs routinely monitored include body temperature, pulse rate, respiration rate, and blood pressure.
Definition
Vital signs are measurements that reflect the body’s most basic functions. They serve as a quick and effective way to evaluate a person’s overall health and can signal the presence of medical conditions requiring further investigation.
Examples
The four main vital signs include:
Body Temperature: This measures the body’s ability to generate and dissipate heat. Normal body temperature typically ranges from 36.1°C to 37.2°C.
Pulse Rate: This indicates the number of heartbeats per minute, providing insights into heart rhythm and strength. A normal pulse rate for adults ranges from 60 to 100 beats per minute.
Respiration Rate: This measures how many breaths a person takes per minute, with a normal range of 12 to 20 breaths per minute for adults.
Blood Pressure: This reflects the force of blood against artery walls during heartbeats (systolic pressure) and between beats (diastolic pressure). Normal blood pressure is considered to be around 120/80 mm Hg.
Factors that can affect your vital signs
Vital signs can be influenced by various factors, including age, physical fitness, emotional state, and underlying health conditions. For instance:
Age: Vital sign norms can vary significantly between infants, children, and adults.
Health Conditions: Conditions such as fever can elevate body temperature, while dehydration may increase pulse rate.
Lifestyle Factors: Stress, anxiety, physical activity, and medications can also alter vital sign readings
MAINTAINING NORMAL VITAL SIGNS
Maintaining overall health can help keep your vital signs within normal ranges. Key factors include:
Regular Health Check-ups: Routine monitoring of vital signs can help detect issues early.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, managing stress, and avoiding tobacco can promote stable vital signs.
Hydration: Staying well-hydrated supports normal physiological functions.
Importance of vital signs
Healthcare providers use vital signs as part of a comprehensive assessment:
Initial Assessment: Vital signs are often the first measurements taken during medical evaluations to establish a baseline for comparison.
Monitoring Changes: Trends in vital sign changes can indicate worsening conditions or responses to treatment.
Emergency Situations: In emergencies, abnormal vital signs can guide immediate interventions.
How can vital signs affect my treatment?
Treatment based on vital sign assessment varies depending on the underlying condition:
Medication Management: For example, antihypertensive medications may be prescribed for high blood pressure readings.
Emergency Interventions: In acute situations where vital signs indicate critical conditions (e.g., severe hypertension or bradycardia), immediate medical treatment may be necessary.
The prognosis associated with abnormal vital signs depends on the underlying causes. Early detection and intervention often lead to better outcomes. For chronic conditions like hypertension or diabetes, regular monitoring of vital signs is crucial for managing health effectively.
How can you keep track of your vital signs?
For individuals with chronic health issues affecting their vital signs:
Self-Monitoring: Patients may be advised to regularlyt check their blood pressure or heart rate at home.
Education: Understanding what constitutes normal ranges for their specific health conditions empowers patients to seek timely medical advice when necessary.
Support Systems: Engaging with healthcare providers for regular follow-ups can enhance management strategies.
What is the way forward?
Lifestyle Modifications: Recommendations may include dietary changes or increased physical activity for patients with abnormal vital signs related to lifestyle factors.